The latest article in our Insight Snapshot series focuses on the NRFC’s Value-add in Resources Priority Area and its role in the energy transition and Australia’s global strategic positioning. Visit our website to read previous Insight Snapshots on our Medical Science and Enabling Capabilities Priority Areas.

Australia’s resources sector has long underpinned our national prosperity.
The sector possesses several competitive advantages compared to our global competitors, including our world-class resource endowment, highly skilled workforce, and trusted record in sustainable production.
This leaves the sector primed to capture the growing demand for critical minerals essential to clean energy, defence, and advanced manufacturing, as well as for technologies that enhance productivity, sustainability, and safety.
The opportunity
Australia is home to some of the world’s largest reserves of critical and strategic minerals, including lithium, cobalt, and rare earths, as well as specialty metals such as vanadium and tantalum that are used to manufacture advanced and low-emission technologies.
| Commodity | World Ranking for Economic Resources | Share of World Economic Resources | World Ranking for Production | Share of World Production |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium | 2 | 28% | 1 | 49% |
| Iron ore | 1 | 31% | 1 | 38% |
| Rutile | 1 | 66% | 1 | 35% |
| Bauxite | 3 | 12% | 1 | 26% |
| Zircon | 1 | 77% | 2 | 24% |
| Gold | 1 | 21% | 3 | 10% |
| Lead | 1 | 37% | 2 | 10% |
| Manganese ore | 4 | 15% | 3 | 9% |
| Uranium | 1 | 32% | 4 | 9% |
| Zinc | 1 | 28% | 3 | 9% |
| Rare earths | 6 | 5% | 4 | 8% |
Note: World ranking for Australian Economic Resources and Australian production as at December 2023. | ||||
Global supply chains for critical minerals are vulnerable due to production being concentrated in a handful of countries, most notably China.
By expanding its critical minerals capacity, Australia can reduce dependence on foreign supply and provide alternative sources for use in domestic industries and allied countries.
Processing critical mineral ores to produce mineral concentrates requires substantial capital and technical expertise to create products that meet the precise specifications of end users. Australia’s plant operators and equipment suppliers already possess strong capabilities in this area, creating opportunities to apply this expertise to new technologies, improved processing methods, and more complex downstream value-adding.
The NRFC will look to invest in businesses that make this shift possible. The aim is to turn resource endowment into industrial advantage and sovereign capability.
The global context
Australia’s strategy to grow the geostrategic and economic benefits of its critical minerals sector is being implemented within a dynamic global landscape. Nations such as the United States, Japan, and members of the European Union are already investing heavily in mineral value add and allied supply chains.
The recently announced US-Australia Critical Minerals Framework, backed by a joint commitment to invest at least US$8.5 billion, exemplifies how partnership-driven investment can accelerate Australian projects such as Arafura’s Nolans Rare Earths Project.
For Australia, this is both a risk and an opportunity. Without local processing, high value industries such as battery manufacturing, renewable energy infrastructure, and electric vehicles will remain offshore. With targeted investment, Australia can become a reliable supplier of refined materials and advanced components to allies and global markets.
Why is resource value-adding important?
Adding value to our mineral resources brings several significant benefits for the Australian economy and our strategic global positioning.
- Critical minerals demand growth: Global demand for critical minerals necessary for the development of clean energy technologies is forecast to quadruple by 2040. Meeting rising global demand for critical minerals positions Australia to capture greater economic returns from our abundant mineral resources.
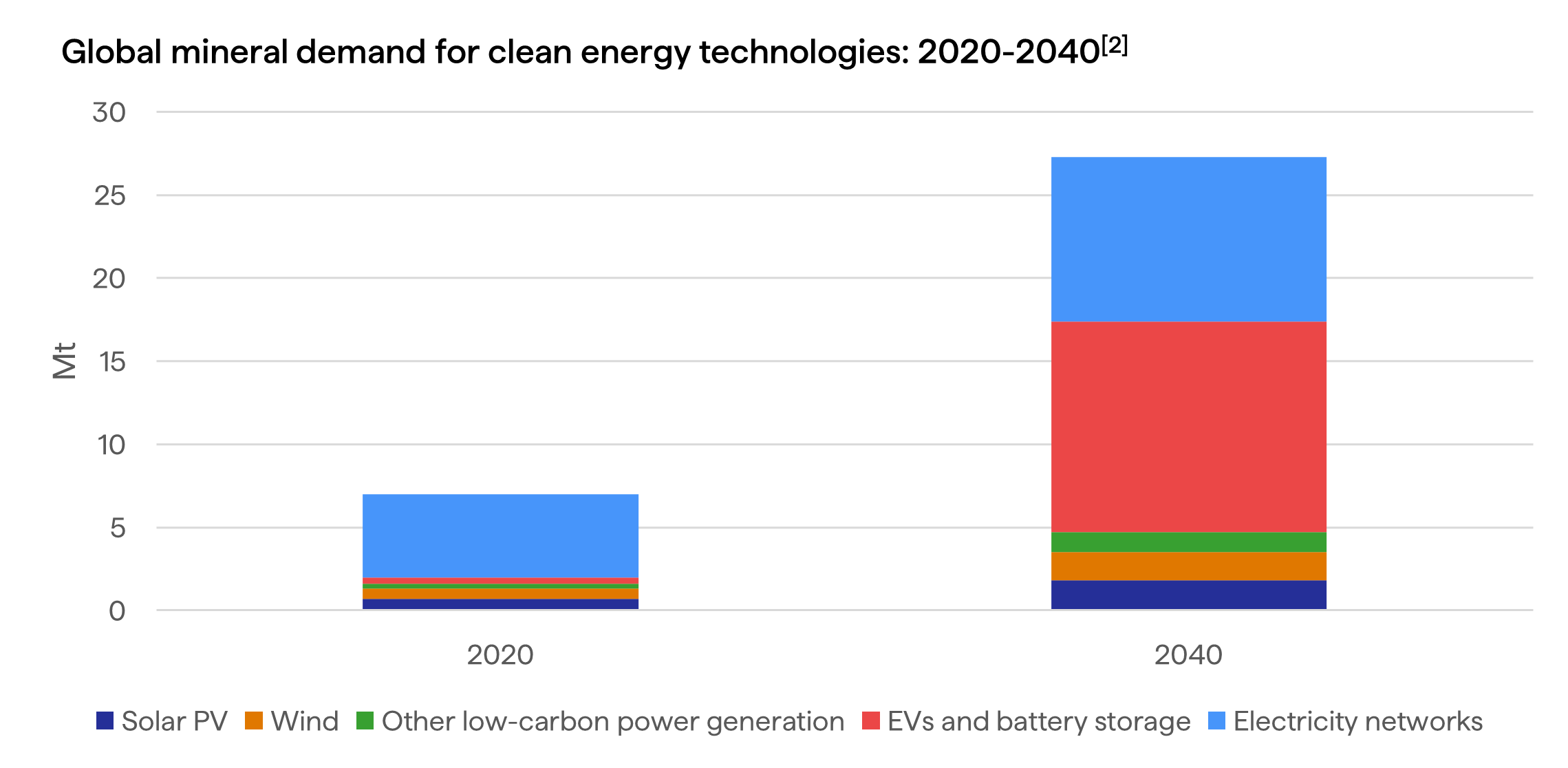
- Regional jobs: Expanding primary and downstream processing supports skilled employment and industrial growth in regional communities.
- Clean energy transition: Producing minerals for use in battery manufacturing and other clean energy technologies domestically strengthens Australia’s contribution to global decarbonisation and clean technology supply chains.
- Economic security: Developing onshore processing reduces reliance on overseas supply chains, enhances sovereign capability, and supports long-term economic resilience.
What does success look like?
- Sovereign capability in critical minerals processing and manufacturing for key technologies.
- Australia extracts more value onshore from our resources – creating jobs and economic opportunity, including for regional and First Nations communities.
- Integrated manufacturing corridors producing battery components, alloys, and specialty metals for domestic and export markets.
- Increased investment from, and collaboration with, likeminded partners to grow Australia’s downstream processing capability and build diverse, resilient, and sustainable global supply chains.
- Growth of Australia’s renowned mining equipment, technology and services (METS) sector.
- Circular economy facilities recovering valuable materials from end-of-life batteries and electronics.
- Regional revitalisation through the creation of additional high skill processing and manufacturing jobs.
What types of resource sector investments is the NRFC looking for?
NRFC financing supports commercially viable companies and projects that:
- refine or process raw minerals into higher value materials
- apply advanced technologies such as automation, robotics, AI-driven process control, and low emission smelting to improve productivity, sustainability, and safety in the resources sector.
- build resilient local and allied supply chains for critical minerals
- deliver environmental performance consistent with national climate goals.
What’s next?
The NRFC continues to engage with industry, research organisations, and investors to identify scalable projects that align with national objectives. The focus is on partnerships that convert natural resource strength into competitive advantage.
Australia has the resources, the expertise, and the policy settings. With strategic investment, it can also have the industrial capability to match.
NRFC investment case studies
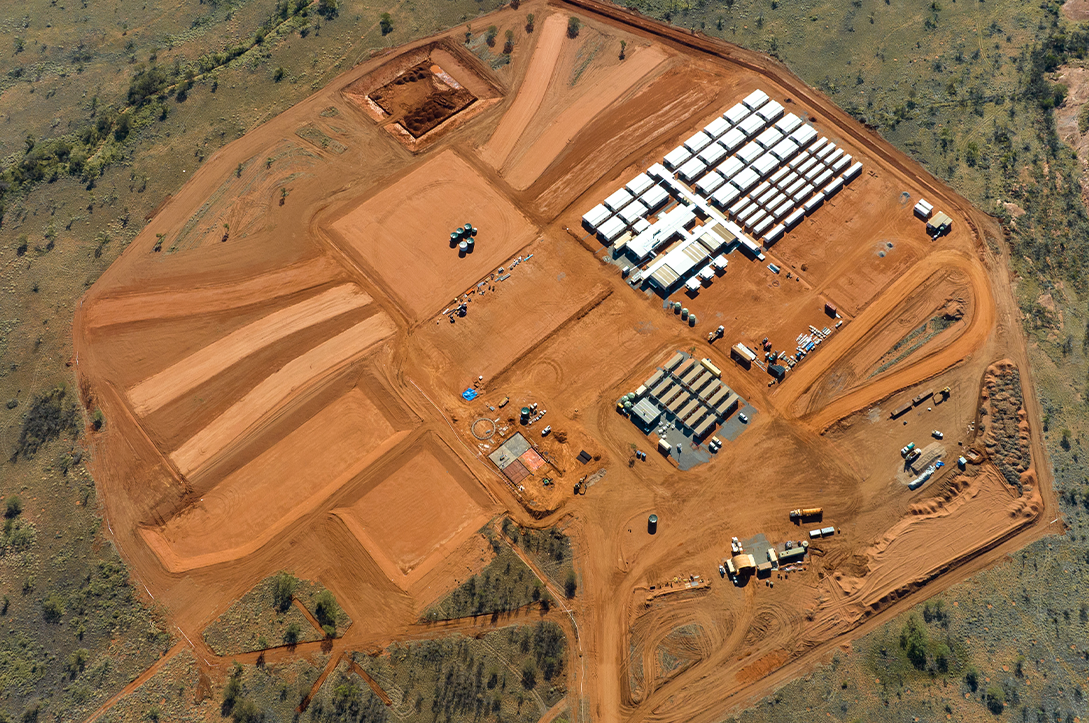

Arafura Rare Earths
The NRFC has made a $200 million investment commitment in Arafura Rare Earths Limited’s Nolans Project, which will produce around 4% of the world’s neodymium and praseodymium demand from 2032.
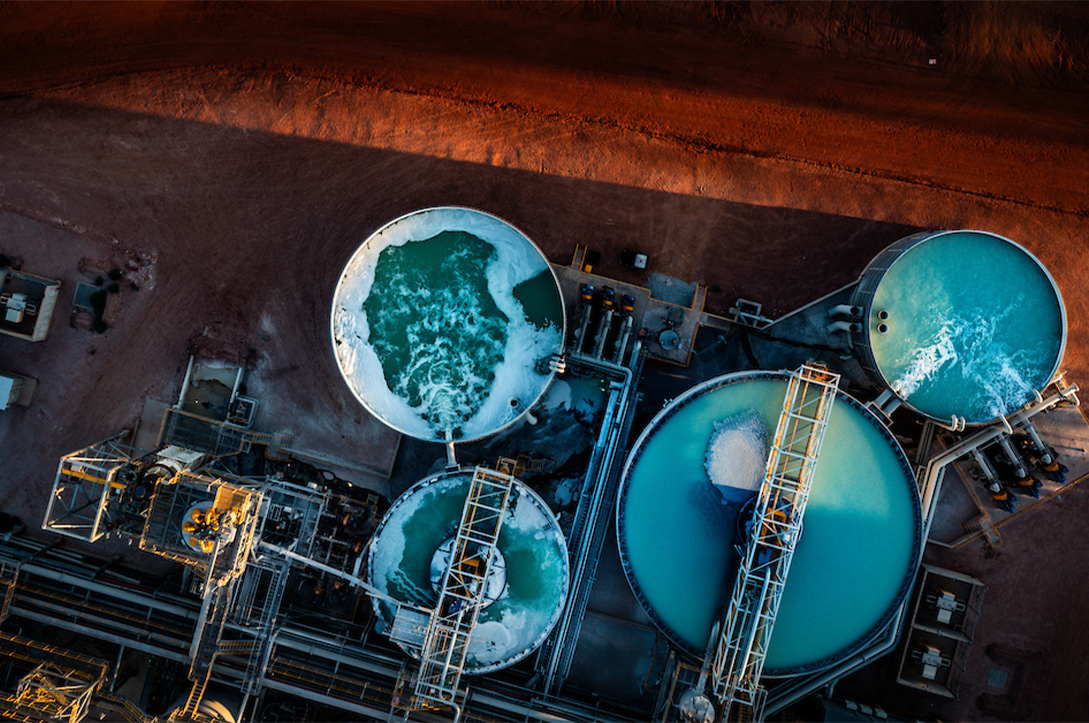

Liontown Resources
The NRFC has made a $50 million investment in Liontown Resources, a lithium producer and refiner whose Kathleen Valley Lithium Operation is expected to produce 500,000 tonnes of spodumene concentrate per annum over the next several decades.
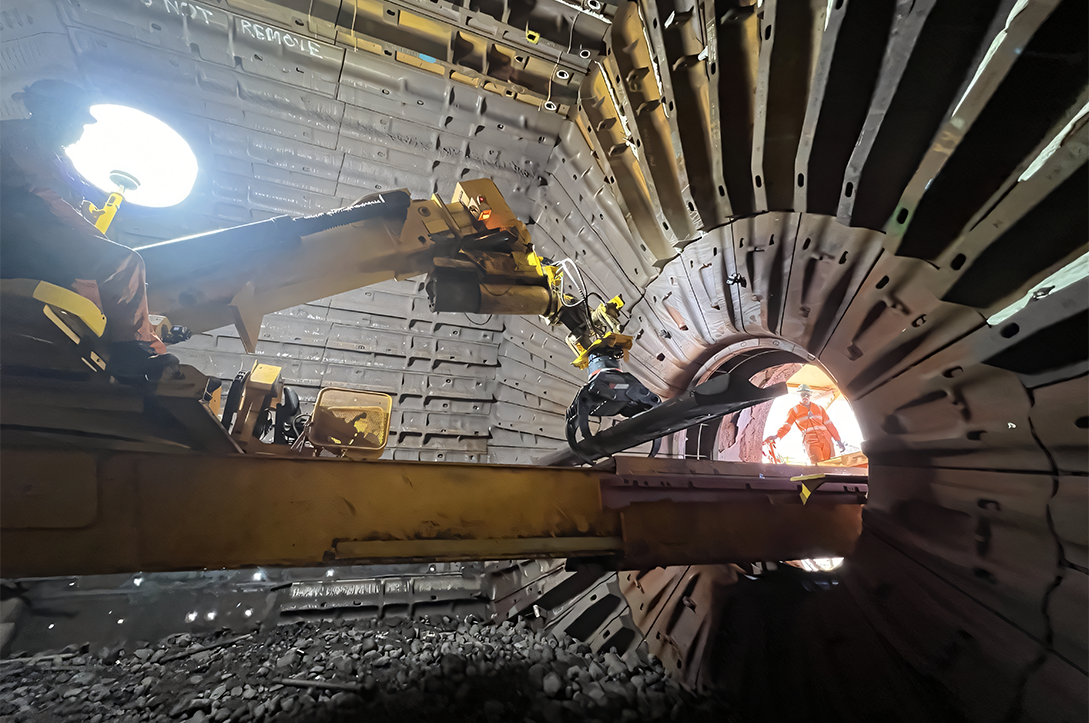

Russell Mineral Equipment
The NRFC has made a $40 million investment in Russell Mineral Equipment, a world-leading manufacturer of mill relining technologies for the mining and minerals processing industry.
Get in touch
Do you have an investment-ready proposal in the Value-add in Resources Priority Area? Read our investment guidance and then contact the NRFC to discuss if your project is eligible for funding and how we can work together to add value to Australia’s mineral resources.
[1] Geoscience Australia, Australia's Identified Mineral Resources 2024 - World Rankings. https://www.ga.gov.au/aimr2024/world-rankings(Opens in a new tab/window)
[2] IEA, 2021. The Role of Critical Minerals in Clean Energy Transitions. https://www.iea.org/reports/the-role-of-critical-minerals-in-clean-energy-transitions(Opens in a new tab/window)

